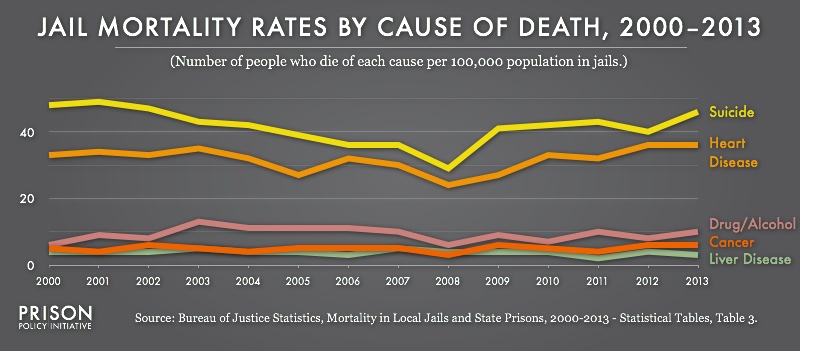
Women celebrate court ruling
Yesterday, Uganda’s Supreme Court ruled that refunding a bride price when customary marriages end is unconstitutional and should be banned: “Refund of the bride price connotes that a woman is on loan and can be returned and money recovered. This compromises the dignity of a woman.” The judges unanimously agreed that referring to bridal gifts as bride price reduces its significance to market value. On the other hand, the judges decided that bride price itself is not (yet) unconstitutional. This victory for women’s rights, power and dignity emerges from the persistent organizing work of MIFUMI, a Uganda based women’s organization that, since its establishment in 1994, has focused on domestic violence and bride price, which, they argue, is a form of structural domestic violence.
In 2004 MIFUMI organized the first international conference on bride price, which produced the International Kampala Declaration on Bride Price. The Ugandan government responded by saying bride price belongs to customary laws and courts.
Undeterred, in 2007, MIFUMI petitioned Uganda’s Constitutional Court, seeking to have “bride prices” declared unconstitutional: “The payment of bride price by men for their wives as demanded by custom from several tribes in Uganda leads men to treat their women as mere possessions from whom maximum obedience is extracted, thus perpetuating conditions of inequality between men and women”. In 2010, the Constitutional Court overwhelming rejected MIFUMI’s petition. MIFUMI appealed to the Supreme Court.
In 2011, leading Ugandan feminist jurist Sylvia Tamale noted, “Strategic action litigation in the area of gender and sexuality is … in its infancy … Its process is brutal and controversial. Most women’s rights NGOs that engage this strategy take their cases to mainstream lawyers due to limited capacity and the fact that most female lawyers shy away from overly aggressive lawyering. This means that lawyers who argue such cases in court lack the requisite empathy with feminist issues and methods … This, for example, happened in the recent Ugandan case of Mifumi (U) Ltd. & 12 Others v. Attorney General & Another (Const. Petition No. 12 of 2010) where the women’s rights NGO, Mifumi unsuccessfully challenged the traditional practice of bridewealth, associating it with domestic violence. Instead of directly challenging the deeply entrenched practice per se, perhaps it may have been more strategic to focus on and argue against its oppressive aspect that requires a wife to `reimburse’ bride price in full in order to gain divorce from her abusive husband.”
A mere four years later, and here’s MIFUMI again, one step closer to full abolition. Leah Nabunnya, a spokeswoman for MIFUMI declared, “The court’s pronouncement is a win for us.” Solomy Awiidi, a legal officer with MIFUMI, agreed, “There are fathers and brothers of brides facing civil suit because they failed to return the bride price, while thousand if not millions of women across the country who have been abused because of failure to refund the bride price. This ruling will liberate many of them.” MIFUMI Director for Communications Evelyn Schiller added, “Women are no longer going to be chained in abusive marriages. They have been given a choice. This court declaration means that women can escape from a marriage if it is abusive without fear that I have to refund the price that was paid for me 20 years ago or that my father and brothers will pay the repercussions for this if I leave this marriage.”
Atika Turner, Executive Director of MIFUMI, concluded: “A woman is turned into an object that is not taken into account during those discussions, she does not have a say in how much is paid. The man feels he is entitled to his wife’s obedience, reproductive capacity and labor. So anytime she resists his demands, he feels he is entitled to mistreat her and this forces many women to endure violence.”
Yesterday’s court decision in Uganda demonstrates the real potential for women’s material liberation everywhere. Women are organizing in the streets, households, courts, conference halls, legislatures, and beyond. Undeterred by impediments, they study the situation, analyze the defeats, and hone their tools and weapons. Thanks to MIFUMI and their sisters everywhere, the struggle continues!
(Photo Credit: United in Beauty)