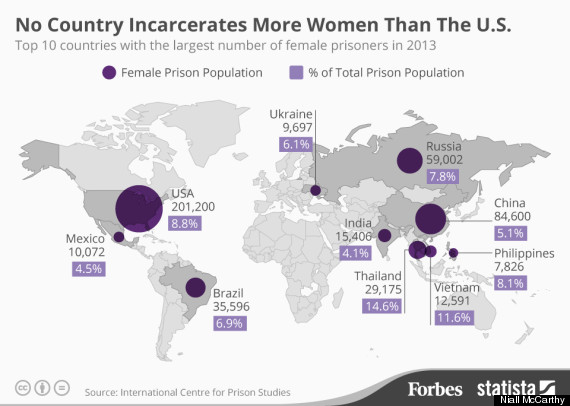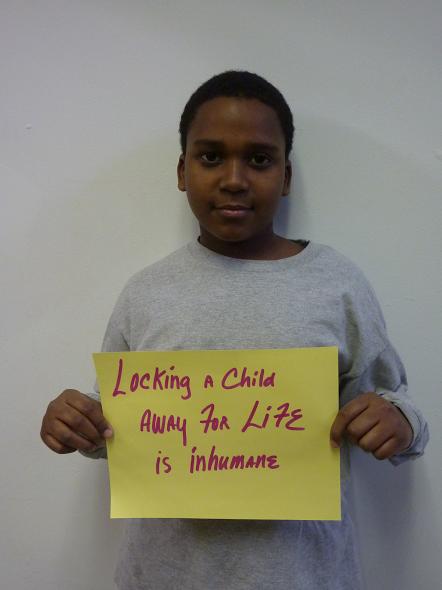
The United States is the only country in the world that sentences children to life without parole. In `America’, when we say life without parole, we mean it. Currently, about 2570 children are serving life without parole. With more than 500 people convicted as juveniles and given mandatory life sentences without parole, Pennsylvania leads the nation and the world in the practice of devastating children’s lives.
Two years ago almost to the day, in Miller v Alabama, the United States Supreme Court outlawed mandatory life sentences without parole for juveniles. The Court did not ban life sentences without parole, but rather chose to ban the mandatory aspect. Three weeks ago to the day, that same Supreme Court refused to hear a case, Cunningham v Pennsylvania, which concerned the retroactivity of their earlier decision. If mandatory juvenile life without parole became wrong, on Constitutional grounds, in June 2012, shouldn’t that Constitutional reasoning apply to all those children who came before and now struggle to survive in an inhumane situation? For the Supreme Court, the time is not right.
The time is not right for many states across the United States. Last week, the Sentencing Project released a report, Slow To Act: State Responses to 2012 Supreme Court Mandate On Life Without Parole, which showed a national reluctance to abide by the Supreme Court mandate. The Supreme Court decision struck down laws in 28 states: “Two years later, the legislative responses to come into compliance with Miller have been decidedly mixed. A majority of the 28 states have not passed legislation. Frequently, the new laws have left those currently serving life without parole without recourse to a new sentence. Though 13 of the 28 states have passed compliance laws since Miller; the minimum time that must be served before parole review is still substantial, ranging from 25 years (Delaware, North Carolina, and Washington) to 40 years (Nebraska and Texas). Most states, not only those affected by Miller, still allow juveniles to be sentenced to life without a chance of parole as long as the sentence is imposed through individual review rather than as a result of a mandatory statute.”
State after States continues to insist that prison is the answer, that a policy of mass despair and death-in-life is the best thing for `some children.’ Juvenile life without parole laws supposedly addressed a sudden eruption of predatory and feral violence committed by incorrigible children. As Deborah LaBelle, Executive Director of the Juvenile Life Without Parole Initiative, has noted, that means Black and Latino.
In Miller v Alabama, the Supreme Court decided that children are children and that children matter. No matter what they do, children are children, and this means, among things, they have a greater capacity for rehabilitation, assuming responsibility, healing and repairing. Mandatory juvenile life without parole denies children their identities as children. All juvenile life without parole denies children not only their existence as children, but also the possibility for all of us that a community cannot be built on the manufacture of despair. Hope matters.
Pennsylvania, despite your legislature and your Supreme Court, take your position as the world’s leading incarcerator of children for life without parole, and turn it inside out. End juvenile life without parole, all juvenile life without parole. Do it now.
(Image Credit: Pennsylvania Coalition for the Fair Sentencing of Youth)