At the beginning of February, His Majesty’s Chief Inspector of Prisons Charlie Taylor issued a report, “The long wait: A thematic review of delays in the transfer of mentally unwell prisoners”. It is predictably dismal and dismaying reading, dismaying not only because of its gruesome details and insights but also because of its lack of surprise. There is no surprise that the prisons of England and Wales are the furthest possible distance from any sense of justice. There is likewise no surprise that the most vulnerable, the ones most in need of assistance and more, are the least served, or, perhaps, the most served with a kind of violence and misery. Here’s the core of the most current report: “Only 15% of patients in our sample were transferred within 28 days and waiting times for a bed were too long. The average wait was 85 days from the point it was identified that their mental health needs could not be treated in prison, with a range of three to 462 days.” By law, anyone deemed in need of mental health care must be, not should be must be, transferred to mental health hospitals within 28 days. In this scenario of lack of, or refusal of, care, where are the women? Again predictably, everywhere and under the greatest threat.
Much of the report involves “men and women”, as in “Our prisons continue to hold a number of very seriously mentally unwell men and women”. But there are moments in which women are at the center of the findings: “I will always remember the deep shock of walking into a unit in Eastwood Park, where acutely mentally unwell women were being held in appalling conditions with bloodstains on the floor and scratch marks on the walls; evidence of the levels of distress of the women being held there …. At Low Newton women’s prison in Durham the screams from the inpatient unit where the most mentally unwell women were held were so distressing that other prisoners told us they were put off going for their medical appointments.”
“I will always remember”. The irony is that, while Charlie Taylor may always remember, the “care” for women who are incarcerated is marked by amnesia and silence. Consider the twelve months prior to the report’s release, and this will be at best a grossly minimal account.
In March, the Independent Monitoring Board issued its Annual Report of the Independent Monitoring Board at HMP/YOI Eastwood Park: “Whilst efforts have been made to reduce levels of self-harm the high number of women being imprisoned with severe mental health issues has been compounded by the impact of lockdown. Eastwood Park is currently considered nationally as a prison of concern.” Repeatedly, the report emphasizes that the prison is now housing an “unprecedented number of mentally unwell and vulnerable women, as well as women with complex needs.” The result is, predictably, “exceptionally high levels of self-harm.” Eastwood Park is currently considered nationally as a prison of concern. Is it? By whom? By the way, this report was widely reported.
On July 27, 2023, the UK Ministry of Justice released Safety in Custody Statistics, England and Wales: Deaths in Prison Custody to June 2023 Assaults and Self-harm to March 2023: “There were 59,722 self-harm incidents in the 12 months to March 2023, up 11% from the previous 12 months, comprising of a 1% decrease in male establishments and a 52% increase in female establishments. Over the same period, the rate of self-harm incidents per 1,000 prisoners, which takes account of the increase in the prison population between this and the previous year, decreased 5% in male establishments but increased 51% in female establishments …. There were 59,722 self-harm incidents in the 12 months to March 2023, up 11% from the previous 12 months, comprising of a 1% decrease in male establishments and a 52% increase in female establishments … In male establishments, self-harm incidents decreased 1% and assault incidents increased 11%. In female establishments, both self-harm and assault incidents increased, by 52% and 16% respectively … The rate [of self-harm] in female establishments has increased considerably by 51% to a new peak (5,826 per 1,000 prisoners), whereas it has decreased 5% in male establishments (523 per 1,000 prisoners), meaning the rate is now more than eleven times higher in female establishments.” These dismal numbers were widely reported.
In the next Ministry of Justice Safety in Custody Statistics report, the investigators found, “The rate of self-harm incidents per 1,000 prisoners, which takes account of the increase in the prison population between this and the previous year, increased 3% in male establishments and increased 63% in female establishments.” This too was widely reported.
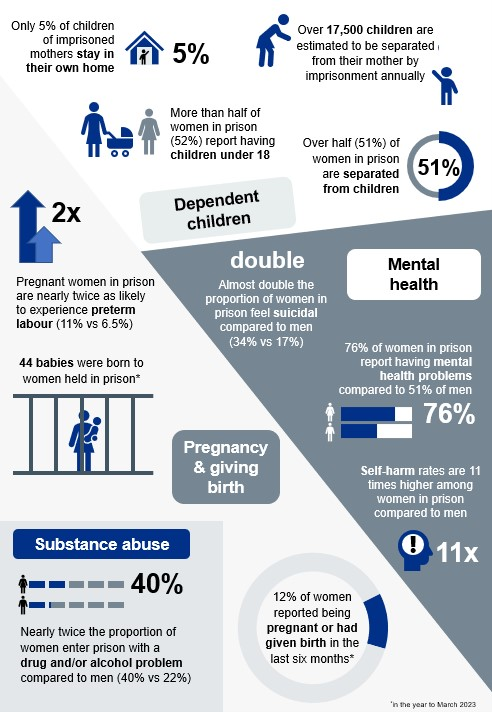
On November 23, 2023, the National Health Service England released its long awaited report, A review of health and social care in women’s prisons. The report, which received widespread attention, stated, “Women in prison have disproportionately higher levels of health and social care needs than their male counterparts in prison and women in the general population. High numbers of women in prison experience poor physical and mental health and many are living with trauma. Findings from this Review further highlight the vulnerability and adverse life experiences of many women in prison. Mothers feel keenly the separation from their children that imprisonment brings, and women who are mentally unwell are still being sent to prison. None of this is new.” None of this is new.
Concerning mental health care, the report noted, “Acutely mentally ill women are still being sent to prison. Prisons are ill equipped to provide the necessary treatment and care for acutely mentally ill women. There is a gap in mental health services across the range of needs including primary mental healthcare and specialist interventions for women who have experienced trauma, including sexual and domestic violence.” This too was widely reported.
There were many more reports, both from the government and from various organizations and news agencies, but the point is made. None of this is new. Reports are only fine if they are read and acted upon. Otherwise, they are worse than empty gestures. They are part of the machinery that is pulverizing women – vulnerable women, women of color, working class women, women living with mental health issues, women living with disabilities, pregnant women, women who are mothers, women – into dust. The women’s prisons are filled with dust. It is a matter of concern. We will never forget … will we?
(By Dan Moshenberg)
(Image Credit: NHS England)
