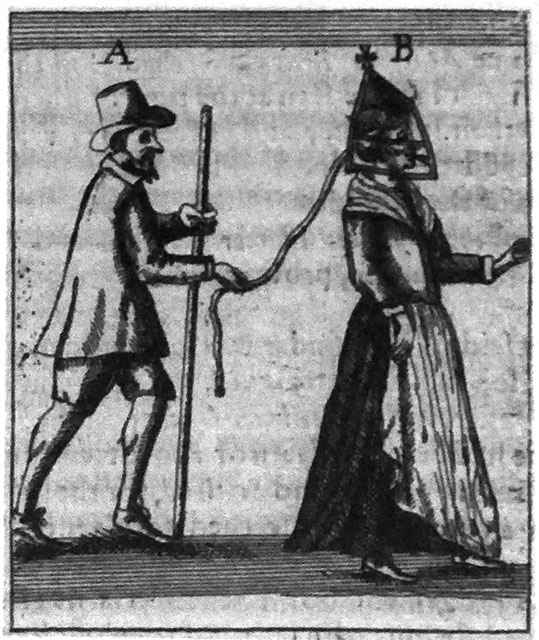
“A scold is paraded through the community wearing the “bridle,” an iron contraption used to punish women with a sharp tongue. Significantly, a similar device was used by European slavetraders in Africa to subdue their captives and carry them to their ships.”
The U.S. Supreme Court recently created a material and spectacular demonstration of how historical occlusions persist in the present. The people who were not the writers of enshrined documents, including those kidnapped from the African continent or related to them, people with disabilities and many others, are, were, and now will be even more so, at the elusive mercy of legislation, institutions, national borders and predilections of race and class.
As Jill Lepore wrote weeks before the overturn, “Women are indeed missing from the Constitution. That’s a problem to remedy, not a precedent to honor… [A woman] herself does not exist but is instead, as Mary Wollstonecraft wrote, a ‘non-entity.'”
Since the onset of the pandemic, the idea of “essential work” has entered a general consciousness in that people who perform tasks that are crucial to the maintenance of life have become relatively more visible. During the pandemic, workers who do the work that has historically and traditionally fallen to women, including food deliverers and caregivers, continued to endure starvation wages. An understanding seemed to emerge that if their numbers thinned, an already en masse health crisis would significantly broaden. And yet, one year after social media bristled over food deliverers being exploited on the front lines of the virus, and days after SCOTUS paved the way to criminalize abortions and miscarriages, a Door Dash worker was shot by police, thereby putting the essential worker ‘back in his place’ of disposability.
I
Such categories of non-status, “hyper-exploited” or “informal” work, as Maria Mies and others have called them, have been barred from the “worker” definition because tasks that were historically assigned to the bodies associated with motherhood are conferred the same lack of prestige imposed onto those who raise or bear children. Even in contexts that talk about subsistence or workers rights, childbearing, domestic labor and multiple forms of informal labor are still not given minimal protections, or even (until recently) sufficient language for describing thankless conditions of work that are, as a matter of course, unacknowledged, erased, and gaslit.
The existence of a femmes, reproductive, and “housewifized” labor form is an historical reality, not a “natural” one. Although biology is largely founded on the idea that only some bodies bear children, the division of labor that surrounds reproduction is a product of historical and social relations; it is not a “natural” condition. That said, the appearance of ‘natural’ gender grants the authority to exploit gendered bodies as a site of experimentation towards the blueprint for mass violence, slavery and trafficking. Mass disposability is a consequence of the decimation of bodily autonomy.
If definitions of the ‘wage-worthy’ have been narrowly defined, then so has value. The war in Ukraine has also posed a considerable threat to the stability of the idea of value. National entities and representatives are currently pouring enormous sums of capital into visions of how future East/West European and world borders will be shaped. Where Russia follows a regime of sacrificing humanity for an abstract border, the West describes and re-describes the value of the human. Whether or not the ‘human’ is truly a concern for Western governing entities or merely a form of propaganda that veils the preservation of future accumulation remains to be seen, but the discourse itself has a public and social effect that has generated many formal policy-making discussions that involve accepting financial losses in the name of boycotts.
It would not be obstreperous to imagine that between the recently circulating iteration of essential labor under covid and the boycott of previously advantageous business deals with Russia, the global socius might be exhibiting a tendency towards evolving away from living and thinking the numerical values of money in the “normal,” linear or historically predictable sense. Even the possibility of such a development represents an unprecedented threat to entities that thrive on and continue to demand unbridled powers of accumulation.
II
In 1847, when Marx wrote the Communist Manifesto in three weeks, he was commissioned by The Communist League, formerly The League of the Just, a group that was largely composed of guild worker artisans. One of the effects of this influential context is that “worker” in many texts still conjures images of White male woodworkers, bricklayers, stair builders and the like. The conditions of the creation of the Manifesto implicate a transition from the relative leverage that skilled guild artisan labor had against capital to the ‘worker hands’ who were tools of production, disposable, unskilled or de-skilled, and stripped of autonomy. Marx’s iteration of the “worker,” forged via a commission by reasonably nervous White male artisans as an expression of their fear of being instrumentalized as cogs, may well have supplied the material for a Right-wing contingent to abuse, in order to construct itself as the “authentic” worker body. This trace of relatively privileged artisans speaking on behalf of a much broader constituent of workers, in a kind of Napoleonic move according to Marx’s own early construction of the idea of class, re-appears in a mutilated and weaponized version in Steve Bannon’s view that the US remains an exploited colony of Europe in which only American-born White men need to be expressed by the “worker” notion. Entitlements to this definition are obviously at the catastrophic expense of others who perform other kinds of work including more essential and more socially occluded forms. The kinds of entitlements Bannon and other such figures easily reference have produced “replacement theory” and its accompanying gun violence, human abuses at borders, and violence in places structured towards xenophobia, as well as other sectors that have copyrighted authenticity in a multitude of dimensions, including but not limited to the arts, i.e., the masculinized elitism of “artistic technique” and so on.
That terms like “sex work” still require the qualifier “sex” in order to be inserted into the category of “work” testifies to an order of ‘true’ workers that obfuscate marginalized laborers and labor forms. Similarly, the work of slave labor in the 18th and 19th centuries, much of it domestic, was not seen as tool-bearing, which is one of the stipulations associated with what defines masculine labor against the feminine embodied labor that Maria Mies analyzed in the 1980s according to “work with the breasts and the womb.” Similarly, the idea of ‘slave’ is constructed as not a person who works, but as an inanimate tool of production in and of themselves, and is as such written out of the labor definition, with these practices carried into the present in prisons, unpaid overtime and the charge of laziness; an accusation that erases the possibility that a person with physical needs, such as sleep, or a psyche is connected to a body that is supposed to magically produce value for someone else without a personal or labor process. In “One is Not Born a Woman”, Monique Wittig links slave labor with gendered labor, arguing that the construction of gendered biology, including assumptions of ‘nurture’ projected onto childbearing bodies, produce invisibility and non-personhood in order to garner and quietly profit from the free labor value of the erased.
Meanwhile, the authentic, normative, standardized idea of “worker” produces a logic through which economies continue to deprive embodied workers, including starving artists, caregivers and others, of both wages and the dignity of personhood. In sum, a White male class to whom such historical texts referred retains a grip over the notion of ‘worker’ while others labor ‘outside’ or ‘behind’ the text and thus the historical and social. However, this recent attention given to essential work during lockdown highlights the possibility of re-distributing value within a regime in which value and visibility are intrinsically enmeshed.
III
The US Supreme Court majority now seeks to more intensively enforce the withdrawal and sanctioning of personhood of the exploited and unremunerated worker, of which one foundational category is the childbearer, and also those whose bodies are theoretically capable of bearing children but may choose not to birth. Much has been written about “back alley” abortions, and the many who have other talents and contributions but will be forced to become mothers and do the work of motherhood, laboring at domestic work without remuneration, and submitting to exploitative work in order to survive. Meanwhile those bodies who reject motherhood will be submitted to consequences that have been ‘updated’ by increased surveillance in the form of any number of high technology wars, mass violence, increased stalking, empowered white supremacist cells, and general forms of social pressure that can ensure the sanctioning of those who do not submit to norms complicit within patriarchal legitimacy. The surrounding structures that socially and institutionally police bodies are far more forceful today than they were when the constitution was written. And since then, multiple disciplines and fields of psychoanalysis and biology have naturalized hetero-procreation as the mandatory center of life, from Freud and Darwin to reddit discussion that anthropomorphize the natural world in terms of the procreative habits of varying species, and ‘riff’ on what “natural” gendered behavior should be according to imperializing whims.
The spectacle of misogyny in the confirmation hearings of Brett Kavanaugh, and Clarence Thomas several decades prior, including the “innocence” campaign waged by Johnny Depp or the general possibility of defamation and non-disclosure agreements for high profile rapists, form but a few of the exemplary chains of formal signs with increasing powers of social composition.
Making abortion less accessible will further conscript women into fields of invisible and unpaid labor, making childbearer bodies vulnerable to raising children at whichever level of poverty the State sanctions. The State has already realized billions of dollars in value in the unpaid labor of childbearers enduring toil in the name of “labors of love,” as well as the exploitative work of reproductive bodies coerced into states of desperation, as Sylvia Federici has pointed out. In her terms, profit from women’s unpaid and exploited labor, including but not limited to the production of future populations of workers, has been used to feed war machines, thereby moulding social reality into ever more virulent patriarchal forms.
IV
In Caliban and the Witch, Federici argues that these conditions are both historical and intentional: it was cheaper for the Catholic Church, who was for centuries the main land and wealth holder in Europe, to pay only a male laborer rather than the family supporting him. The Church thus organized the family unit and laws pertaining to the body, including marriage, accordingly. This meant that the wives of man-laborers, the people performing maintenance (food production and preparation, childcare, care for the sick and elderly, mental support) as support for the productivity of their wage-receiving husbands, and also caregiving, material tasks, and the work of the body involved in producing the next generation of workers, would never receive their own wage. By being naturalized into biology, the law-holding theistic institution that operated as the main boss and master, created an exploitation economy that has sprawled outward to consume almost all informal and marginalized labor forms. The production of a culture of silence around forced birth and all of the fallout that will follow for the lives of apparently ‘capable’ childbearing bodies will also have consequences across the entire informal labor economy, and for all genders therein.
In Federici’s account, the Church responded to the scarcity of workers in Europe as a result of the Plague by producing policies to benefit the maintenance of church properties and functions that required a plethora of human capital, and thus a social reality built on procreation. In order to create this economy of its own self-interest, the Church walled off common lands that had previously been used for autonomous food production, and created laws around sex, sodomy (ie non-procreative sex) and childbirth. This counter revolution over decades finally managed to force into submission a heretic movement of people who lived relatively more similarly to the so-called autonomies of current life in atheistic and non-fundamentalist contexts.
The Gutenberg Bible emerged to popularize, naturalize and sacralize the family unit and heterosexual marriage, to construct childbearing as the center of social reality in order to enforce procreation and therein the production of human capital.
Abortion has never been fully sanctioned or supported in the US. And yet, given the recent visibility of workers who served to protect and maintain life in the context of the pandemic, it seems no accident that the traditionalists further sanction the life necessities of bodies in this moment of the coronavirus, in which normally invisible forms of labor, including the toil of the body and the costs to the body in health and vitality, are being obviated. Such a sea change in what constitutes valuable and remunerable work would threaten the very basis of the profiteering economy. Moreover, the Church’s protocols, laws and doctrines that produced imperialization over the body, from the walling (‘hedging’) off of common lands to the sodomy laws to the mandate of ‘a marriage between a man and a woman,’ enforced domestic labor and forced birth, were all created during the plague; in the wake of an ebb of labor power in the context of mass death, illness and a worker re-thinking of the value of life over toil and submission. The historical reality of the plague bears similarities to the conditions produced by covid. The pandemic has intensified fundamentalist logic and brought to the fore the 500-800 year old period in which the Church began to realize its need for labor power/workers by re-organizing all elements of economy and a mutually composing social reality, including the relations of production of the present and the reproductive body as the key to controlling the labor relations of the future, especially the unborn worker. According to Federici, racism and misogyny also had to be created in order to keep laborers from uniting in protest, and people with wombs from controlling the future worker population, not only in number but also in temperament.
The fundamentalism that sees reproduction as profit in the form of unborn laborers is not interested in the personhood of women. Neither healthcare nor consent matter or are considered the responsibility or in the interest of the Christian State. While non-fundamentalist views understand forced birth as fiscally catastrophic as a result of what a multi-dimensional influx of traumatized bodies will cost, the traditionalists have a totally different calculation of profit, a different understanding of labor power, and of human aim. The fundamentalist algorithm of accumulation and functionality excise factors that non-fundamentalists find essential. It’s because of a calculation that ignores State responsibility for human life, leading to institutionalized rape and death and privation for religious aims, that even the most dogmatically capitalist arguments that are non-fundamentalist can find no equivalence or commensurability or appeal even along the most material or profiteering lines.
V
Bodies with the capacity to bear children are not responsible for the fact that they are fetishized for sexual abuse across the globe. Along with the elderly, people with disabilities and children, (all of whom are being raped in the Ukraine along with a program that targets everyone), people who get pregnant will suffer an increase in long term material consequences. What emerges in the next 20 years in Poland and the US after rape victims have been forced to bear the children of extreme trauma will shed light on the catastrophe such policies produce. One can only hope that the children of trauma and forced birth will not be compliant in perpetuating such a regime in the future, and that being born out of trauma will produce for them an alternative rather than static vision for the future.
Poland’s forced birth program is directly relevant to the US situation because, in the few States that offer rape exemptions, making use of them will be predicated on the safety of coming forward. A social reality that does not permit abortion is unlikely to provide a safe environment for rape victims to become vocal. Forced birth will strengthen masculine power by making sexual relations higher stakes and by making rape into a more lasting form of abuse, offering the rapist long term control of his victim. By re-instating a culture of shame, and by enforcing the mother role, the family unit, silent suffering and a rigid social experience will bring the capacity to ‘breathe’ well beneath the minimum at which it currently functions.
Women who are rape victims in particular along with any other abortion seekers have not consented to life with a child. The ruling is a crucial violation of life. Those who cannot abort are likely not to have the means or the mental and physical ability for such a life. Within the context of trauma, the State has an opportunity to steer the fate of children too damaged to perform any but the most exploitative labor, to also hyper-exploit mothers living in a state of desperation, or a subsequent population cut off from its familial culture by trauma, to untether and unmoor subjects in order to make them afresh as productive labor aka potential “tabula rasa” for State purposes. In this context, social networks will be necessary to help traumatized children withstand being alive as critical readers rather than menial cogs, and to create collectives of belonging that hold them away from a violent fate of disposability masquerading as depression, ideation or religious fundamentalism.
Materialist feminists have long observed that calculations of demographics place statistics of predicted pregnancies in relation to immigrant influx and other controls pertaining to material economy. Policies relating to abortion and what social discourse shames or encourages, and how that is engineered across forms of current media or in more historical or medieval forms of advertising, are generally steered by how heads of State require a work force or allocate resources. These practices of analysis for the purpose of policy are not dissimilar to the ideology of war in which the body and the human are subjugated for abstract experiments based on human predictions with unknown outcomes.
VI
The US has long fought over abortion as one of the last frontiers of bodily autonomy after what were reintroduced later as ‘rights,’ separated, severed, alienated via preciousness, specificity and class selection, and annihilated in Europe before the Enlightenment. In recent decades, the US holds immigrants at borders as it “processes them” while making considerations about whether to let them in based on demographics. If a class of mostly Black and Brown people too poor to travel to liberal States for abortions is forced to reproduce, the US can shut down its borders without losing out on the global competition for human capital.
Maria Mies summarized how programs such as forced birth are only limited to being misogynistic at their beginning. She wrote extensively on how bodies that have the capacity to bear children were targeted for the State’s experiments in exploitation, to be implemented later in different forms across broader swaths of population. Every non-capital owning body should become aware that policies of forced birth foreshadow an oncoming onslaught of aggression by owners of capital that will produce more categories of intensively exploited labor, that are likely to effect even privileged classes of the iterated White worker who meets the standard definition. It is here that ‘replacement theory’ must stand in as an alibi for the declining labor conditions of the heretofore relatively privileged White worker who uses this notion to retain a position as ‘the authentic’ as his own material stability crumbles.
I suggest that we turn to materialist feminism and its analysis of the evolution of gender constructs in relation to profit. For what Mies calls “time lag feminism,” or the body of work supporting the idea that women need to ‘catch up’ to men, or the idea of a linear history that ought to progress rather than ‘turn back’ can only yield short term gains in the endless tennis match that was designed by the Enlightenment to ensure that a regime of personality cults, class and identity hierarchies remain static. The idea that women are a generation ‘behind’ men constitutes a kind of white feminism in which women seek to supplant men in a machine that is built by imperializing desires and values.
Analyses might henceforth begin with the understanding that traditions are not going to protect the people they promise to exclude. The labor movements of the left must begin to take gender and reproduction much more seriously as intrinsic to how accumulation and profiteering maintain themselves, placing at the fore the understanding that reproduction is future labor power. Consent is also a crucial barometer for how to resist the historical and ideological imperialization with which the church has had a long-term agenda for recomposing a brutally disciplined and imperializing social reality. Consent literally checks in with the habitability of the body as well as its psychic and immaterial requirements.
Any movement that fails to understand that the battle to own and commandeer reproduction is the battle to own the labor, profit and accumulation of the future, and any movement that fails to understand the nuanced relationship between exploitation and consent is doomed to not only fail, but to play into the hands of imperial reality ad infinitum.
(Thanks to Cedrik Fermont for our conversations pertaining to the fact that every sexual identity has been raped in Ukraine, and the impact of abortion law in Poland for childbearing bodies.)
(By Dora Bleu)
(Image Credit: Caliban and the Witch)